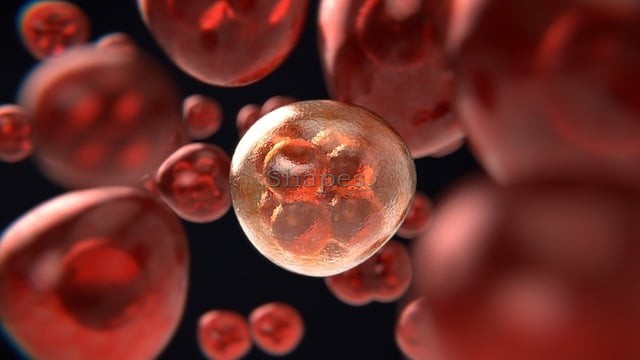
What Are Cancer Cells?
The best Food fighting cancer cells
- Apples.
- Berries.
- Cruciferous vegetables.
- Carrots.
- Fatty fish.
- Walnuts.
- Legumes.
- Supplements and medications.
How Does Cancer Develop?
Cancer is a disease that arises due to genetic changes that affect the way our cells function and multiply. These changes can happen due to various reasons such as errors during cell division, exposure to harmful substances like tobacco smoke and UV rays, or inheritance from parents. The body usually eliminates cells with damaged DNA, but this ability decreases with age, leading to a higher risk of cancer later in life.
Every individual’s cancer has a unique set of genetic changes, and as it progresses, more changes occur. Even within a single tumor, different cells may have different genetic alterations.
Types of Genes that Cause Cancer
Cancer is caused by genetic changes that affect three different types of genes: proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and DNA repair genes. These changes are considered “drivers” of cancer. Proto-oncogenes are responsible for normal cell growth and division, but when altered or too active, they can become cancer-causing genes. Tumor suppressor genes play a role in controlling cell growth, and changes to these genes can lead to uncontrolled cell division. DNA repair genes are involved in fixing damaged DNA, and mutations in these genes can cause additional mutations and changes in chromosomes that may lead to cancer. Researchers have identified common mutations in many types of cancer, and there are now cancer treatments that target specific gene mutations, regardless of where the cancer originated.
Cancer Cells vs. Normal Cells: How Are They Different?
Is there a difference between cancer cells and cancer? Normal cells possess standard DNA and the typical count of chromosomes. However, cancer cells tend to carry an unusual number of chromosomes, and their DNA becomes more and more abnormal due to multiple mutations. Certain mutations are known as driver mutations, as they are responsible for causing the cell to become cancerous.
Conclusion
Eat the best fruits and vegetables – Apples, Berries, Cruciferous vegetables, Carrots, Fatty fish, Walnuts, Legumes, Supplements, and medications, and cut down on sugar as much as possible. Cancerous growths can spread to other parts of the body and invade surrounding tissues, which is called metastasis. These tumors are called malignant. Benign tumors, on the other hand, can be removed without fear of regrowth as they do not spread. While some benign tumors can be large and cause symptoms, they are not as dangerous as brain tumors. It’s worth noting that not all cancers produce solid tumors, and leukemia is an example of a blood cancer that doesn’t.
Cancer is caused by genetic changes in certain types of genes that control cell growth and division. These genes are known as proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and DNA repair genes. Proto-oncogenes, when altered or too active, can become cancer-causing genes, allowing cells to grow and survive when they shouldn’t. Tumor suppressor genes help control cell growth, and any changes to them can cause uncontrollable cell division. DNA repair genes fix damaged DNA, and mutations in these genes can cause additional mutations and changes in chromosomes, leading to cancerous cells. Scientists have found that specific mutations are common in many types of cancer, and there are now several treatments available that target these mutations. Some of these treatments can be used for anyone with the targeted mutation, regardless of where the cancer began to grow.

